What is Cloud Computing? Complete Guide
Published: 3 Sep 2025
In today’s digital world, cloud computing is everywhere and plays a crucial role in our everyday lives. But what is cloud computing? It is the use of the internet to store and access data and programs instead of your computer’s hard drive.

So, guys in this article we will cover the basics of cloud computing, its benefits, and how it is transforming the way we use technology.
I’m starting with the brief history of the cloud, then we will move forward to the intended topic, “What is cloud computing?” Let’s dive in!
History of Cloud Computing
The history and evolution of cloud computing shows how technology has advanced over the years. So, here is the brief history of cloud computing.
Early Concepts and Origins
- John McCarthy, a computer scientist, came up with the idea of cloud computing in the 1960s.
- He said that computers could be run like water or power services for the public.
- This idea was ahead of its time, but it opened the way for new ideas in the future.
- The internet and virtualization technology made it possible for many people to share a single real resource in the 1990s.
- This was an important step toward modern cloud computing.
Key Milestones in the Development of Cloud Computing
- 2000s: Amazon Web Services (AWS) launched in 2006, providing on-demand computing resources and storage over the internet. This was a significant milestone as it made affordable cloud services widely available.
- 2010s: The introduction of other major cloud platforms, like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform, expanded the options and capabilities of cloud computing.
- Present: Today, cloud computing is used for everything from running applications and storing data to providing AI and machine learning services, highlighting its importance in the tech world.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a way to deliver IT services over the internet, allowing users to access data and applications from anywhere without needing physical hardware. For example, services like Google Drive let you store files online and access them from any device with internet access.
Key characteristics of cloud computing include:
- On-demand availability: meaning you can get the services whenever you need them
- Internet-based access: so you can connect from anywhere.
This model makes it easier and more flexible to use IT resources, as you don’t have to worry about managing hardware or infrastructure.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
Cloud computing works by using a network of remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process data. Instead of storing files on your computer’s hard drive, you store them on these servers.
When you want to use a file or application, you connect to the internet and access it from the cloud.
Here’s a simple way to understand it using Google Drive as an example:
- Storage: When you save a document in Google Drive, it gets stored on a server far away, managed by Google.
- Access: To open that document later, you connect to the internet and log into your Google Drive account. The service retrieves your document from its server and lets you view or edit it.
- On-Demand: You can do this any time you want, from any device with internet access.
This makes cloud computing very convenient because you don’t need to carry around storage devices or worry about losing your data if your computer crashes. Google takes care of the maintenance and security of the servers, so you can focus on using the services.
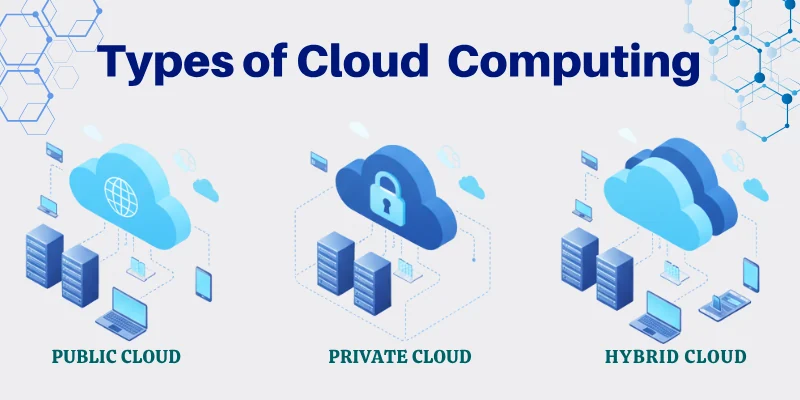
Types of Cloud Computing
There are four main types of cloud computing:
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
- Community Cloud
Within these deployment models, there are four main services: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service (SaaS), and serverless computing.
Here is a brief explanation of types of cloud computing.
1. Public Cloud
A public cloud is operated by third-party providers who offer computing resources like servers and storage over the internet. It’s accessible to multiple users and organizations. Example: Dropbox provides a public cloud service where users can store and access files online from any device with internet access.
2. Private Cloud
A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization and is not shared with others. It offers greater control, customization, and security compared to public clouds. Example: Many government agencies use private clouds to store sensitive citizen data securely, accessible only to authorized personnel.
3. Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud environments, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. Example: A company uses a hybrid cloud to host its customer-facing website on a public cloud while keeping proprietary customer data in a private cloud for security.
4. Community Cloud
A community cloud is shared by several organizations with common interests, such as regulatory requirements or industry standards. Examples: Healthcare providers use a community cloud to share patient records securely among hospitals and clinics.
Cloud Computing Use Cases
Cloud computing has various applications that benefit different sectors. Let’s explore how businesses, education, healthcare, and personal users utilize cloud computing.
1. Businesses and Enterprises
Examples of cloud adoption in various industries:
- Retail: Companies use cloud services to manage inventory, process payments, and improve customer experiences.
- Finance: Banks and financial institutions use the cloud for secure online banking, fraud detection, and data analytics.
- Entertainment: Streaming services like Netflix use cloud computing to deliver movies and shows to millions of users worldwide.
Benefits for small and large businesses:
- Cost Savings: Businesses save money on hardware and maintenance by using cloud services.
- Scalability: Companies can easily scale their resources up or down based on demand, without investing in physical infrastructure.
- Accessibility: Employees can access data and applications from anywhere, improving productivity.
2. Education and Research
Cloud solutions in academic institutions:
- Data Storage: Schools and universities use cloud storage to keep student records, course materials, and research data.
- Virtual Classrooms: Cloud platforms enable online learning, allowing students to attend classes and access resources remotely.
Facilitating research and remote learning:
- Collaborative Tools: Researchers can use cloud-based tools to collaborate with colleagues worldwide in real-time.
- Data Analysis: Cloud computing provides the power to analyze large datasets quickly, helping in scientific discoveries and innovations.
3. Healthcare
Cloud applications in health information management:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): Cloud-based EHR systems store patient information securely, making it accessible to healthcare providers when needed.
- Telemedicine: Doctors can consult with patients online, using cloud-based platforms for video calls and sharing medical data.
Enhancing patient care and data analysis:
- Improved Access: Patients and doctors can access health records from any location, ensuring timely care.
- Advanced Analytics: Cloud computing helps analyze patient data to improve treatment plans.
4. Personal Use
Cloud services for personal storage and productivity:
- Storage: People use cloud services like Dropbox, Google Drive, and iCloud to store photos, documents, and other personal files.
- Productivity Tools: Applications like Google Docs and Microsoft Office 365 allow users to create, edit, and share documents online.
Examples:
- Dropbox: Provides cloud storage for files, making them accessible from any device.
- Google Drive: Offers storage and a suite of productivity tools like Google Docs, Sheets, and Slides.
- iCloud: Apple’s cloud service that syncs photos, files, and app data across all Apple devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
As you guys know, each technology has its benefits and limitations, and the same is true with cloud computing. So here are the major pros and cons of cloud computing:
Benefits of Cloud Computing:
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need to buy expensive hardware and software.
- Scalability: Easily adjust resources based on demand without over-investing in physical infrastructure.
- Accessibility: Access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Collaboration: Enhances teamwork with data sharing and communication tools.
- Automatic Updates: Regular software updates are managed by the cloud provider.
- Disaster Recovery: Simplifies data backup and recovery processes, ensuring data safety.
- Environmental Benefits: More efficient use of resources can reduce the overall environmental footprint.
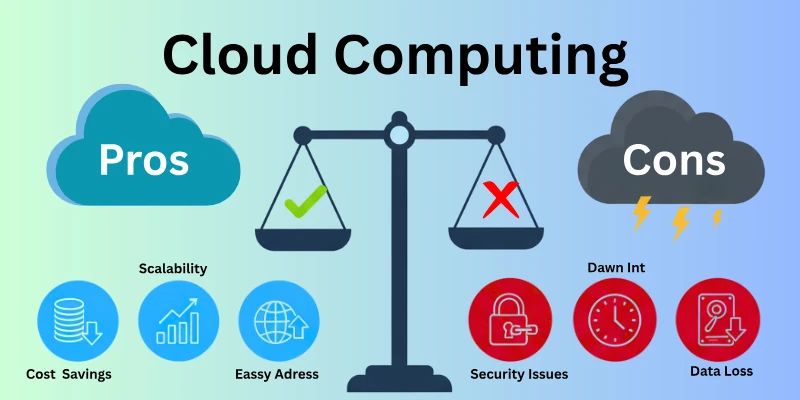
Limitations of Cloud Computing:
- Security Concerns: Storing data off-site introduces potential security risks and privacy issues.
- Internet Dependency: Requires a stable internet connection for access, which can be a problem in areas with poor connectivity.
- Limited Control: Users have less control over the infrastructure and some technical aspects managed by the cloud provider.
- Downtime: Potential for service outages or downtime, which can disrupt access to data and applications.
- Cost Over Time: While upfront costs are lower, long-term costs can add up, especially if the pricing model is not managed carefully.
- Data Transfer Speed: Uploading and downloading large amounts of data can be slower compared to local storage.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is evolving with exciting new trends. It is integrating with advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT), which help computers learn from data and connect everyday devices to the internet.
Experts predict more businesses will use the cloud for its cost savings, with a focus on enhanced security, more effective technologies. Moreover, many companies will adopt hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, combining private and public clouds to meet their needs.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve talked a lot about cloud computing, from where it started to where it’s going. Now, think about how using cloud services could help you in your daily life or work
Have you ever tried them? Share your thoughts or stories about using cloud computing! What do you think about its potential benefits? Let’s discuss and explore the possibilities of cloud technology together.
FAQs
Here are some of the most commonly asked questions related to what is cloud computing:
Yes, cloud computing can be secure when the right protections are in place. Most providers use strong security tools like encryption, firewalls, and access controls. They also update their systems often to block new threats. Still, users must also follow best practices, like strong passwords, to stay safe.
Cloud computing removes the need to buy expensive hardware or set up large data centers. Instead, businesses only pay for the resources they actually use. This pay-as-you-go model reduces upfront costs. It also allows companies to scale without big investments.
Popular examples include Dropbox for online storage and Google Workspace for productivity tools. Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers virtual machines and many other services. Microsoft Azure and iCloud are also widely used. These tools help both individuals and businesses work more easily.
Cloud computing is not only for businesses. Individuals can use it to store photos, music, and documents online. Services like Gmail, iCloud, and Google Drive are everyday examples. It makes life easier by giving access from anywhere.
Cloud computing keeps data stored safely off-site. If a business faces hardware failure, cyberattacks, or natural disasters, files can be quickly restored. This reduces downtime and protects important information. It offers a faster and more affordable way to recover.
There are four main types of cloud computing services. A Public Cloud is shared by many users, while a Private Cloud is dedicated to one business. A Hybrid Cloud mixes both for flexibility. A Community Cloud is shared by organizations with similar needs.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks