Types of Arrays in C++: Beginner’s Guide
Published: 22 Sep 2025
In C++ programming, arrays play an important role in managing data by grouping similar values. But did you know that C++ has multiple types of arrays, each designed for different tasks?
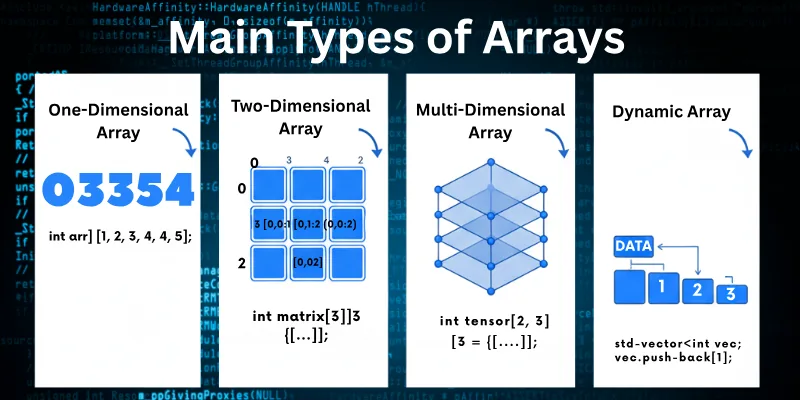
From simple one-dimensional arrays to complex multidimensional arrays, learning about the types of arrays in C++ opens up a world of organized and efficient programming solutions.
But before we explore the world of array types, let me clarify the basic definition of arrays and how they work.
What is an Array?
An array in programming is a tool that helps us store many pieces of information together in one place. Think of it like a row of boxes. Each box in the row can hold one item, like a number or a word. If you collect toy cars, for example, you could put each car in its own box, and line up the boxes in a single row. This way, all your toy cars are organized and easy to find.
In programming, an array works the same way. It keeps all items in one line, and we can access each item by looking at its position in the row.
Example in C++:
int scores[5] = {85, 90, 78, 92, 88};
In this code:
- scores is the name of our array.
- [5] tells us there are 5 spots in the array.
- {85, 90, 78, 92, 88} are the scores that are stored in each spot.
How Do Arrays Work in C++?
In C++, arrays are stored in a line of “memory slots.” Each slot has a special position called an “index” or “address.” Imagine a row of numbered lockers, where each locker can hold one item. If we want to find something, we just look at the locker number. The first spot in an array has the index 0, the second spot has index 1, and so on.
When we need an item, we call it by its index number. This way, we don’t have to search; we just look directly at that spot.
Example: Let’s say we have an array for ages:
int ages[3] = {12, 15, 14};
To get the age in spot 1, we type ages[1]. This will give us 15 because it’s in spot 1.
Main Types of Arrays in C++
There are three main types of arrays in C++:
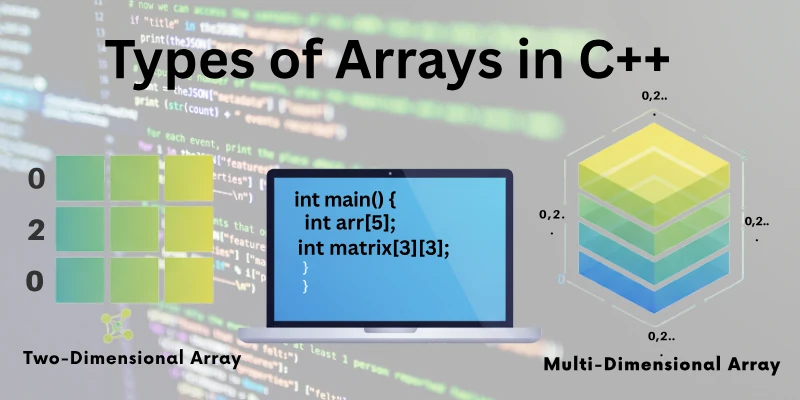
- One-dimensional Array
- Two-dimensional Array
- Multidimensional Array
1. One-dimensional Array
A one-dimensional array, also called a 1D array, is the simplest type of array. It stores values in a straight line, just like a row of boxes. Each spot in the row can hold one piece of data. You can use a one-dimensional array for things like a list of favorite foods, scores in a game, or a list of colors.
Example in C++:
int scores[5] = {85, 90, 78, 92, 88};
In this array:
- scores is the name of the array.
- [5] tells us there are 5 spots.
- Each score goes into one spot in the row, and we can get each one by calling its spot number.
Real-Life Connection
Imagine a grocery list where each item is written in one straight line. You don’t need rows or extra layers, just a simple list. A one-dimensional array works in the same way by keeping things in a straight line.
2. Two-dimensional Array
A two-dimensional array, or 2D array, is a little more complex. It has rows and columns, like a table or a grid. Imagine a seating chart in a classroom. Each student has a specific seat in a row and column, and we can find each one by looking at the row and column numbers.
Example in C++:
int seatingChart[3][3] = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6},
{7, 8, 9}
};
In this example:
- seatingChart has 3 rows and 3 columns.
- Each number represents a different seat.
- If we want seat 5, we look at row 1 and column 1 (because counting starts from 0).
Real-Life Connection
Think of a chessboard with rows and columns. Each square on the chessboard has a row and a column number, and we can find any piece by looking at its position in the grid. A two-dimensional array organizes data in this grid-like way, making it easy to find each item based on two positions.
3. Multidimensional Array
A multidimensional array is an advanced type of array that has more than two rows and columns. The most common one is a three-dimensional array, or 3D array. This array stores data in three directions, like a building with floors, rooms, and items in each room.
Example in C++:
int building[2][3][4] = {
{{1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10, 11, 12}},
{{13, 14, 15, 16}, {17, 18, 19, 20}, {21, 22, 23, 24}}
};
In this code:
- building has 2 floors, each with 3 rooms, and each room has 4 items.
- If we want to find item 20, we go to the second floor, the third room, and the fourth item.
Real-Life Connection
Think of a hotel with multiple floors. Each floor has rooms, and each room has items like a bed, TV, or desk. If you know the floor, room number, and item, you can easily find what you need. A three-dimensional array keeps track of data in this organized way.
Special Types of Arrays in C++
Here are some of the other special arrays types:
1. Character Arrays
A character array holds letters or text. In C++, this is also called a “string.” Each letter is stored in its own spot, and when put together, these letters form words or sentences. Character arrays are useful for names, words, or phrases.
Example in C++:
char word[6] = “Hello”;
In this example:
- word is the array’s name.
- [6] shows it has 6 spots.
- Each letter in “Hello” goes into its own spot in the array.
Real-Life Connection
Imagine a row of blocks, each with a letter on it. When you line them up, they form a word. A character array works the same way by storing letters in order to create words or phrases.
2. Boolean Arrays
A boolean array stores values that are either true or false. Boolean values answer yes-or-no questions, and are useful when we only need to know if something is true or false, like if a seat is taken or a box is empty.
Example in C++:
bool seats[5] = {true, false, true, true, false};
In this example:
- Each spot shows if a seat is taken (true) or empty (false).
Real-Life Connection
Think of chairs at a movie theater. If a chair has a person, it is taken (true). If it’s empty, it’s free (false). A boolean array helps keep track of this information easily.
3. Array of Pointers
An array of pointers is an array where each spot holds an address instead of a direct value. Each pointer in the array points to a memory location.
Example in C++:
int x = 5;
int y = 10;
int *pointerArray[2] = {&x, &y};
In this example:
- pointerArray holds the memory addresses of x and y.
- Pointers are advanced and are used when we need to work with memory addresses directly.
Working with Arrays in C++
Here is the working with different arrays in C++:
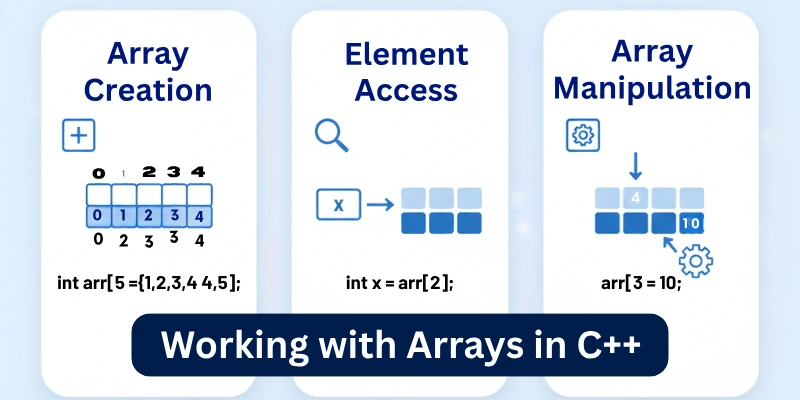
1. Array Initialization
When we create an array, we can fill it with values right away, which is called “initializing” the array.
Example in C++:
int ages[3] = {10, 12, 14};
In this example:
- ages starts with values of 10, 12, and 14 in each spot.
2. Accessing Array Elements
Accessing an element means taking a single value from the array. We do this by using the index or position number of the spot.
Example:
int scores[3] = {95, 88, 76};
cout << scores[1]; // Prints 88
Here, scores[1] gives us the value in spot 1, which is 88.
3. Updating Array Elements
We can change values in an array by setting new values in each spot.
Example:
int numbers[3] = {1, 2, 3};
numbers[2] = 10;
Now, numbers[2] holds 10 instead of 3.
4. Looping Through Arrays
When we need to check every value in an array, we use loops. A for loop is helpful for this.
Example in C++:
int grades[3] = {85, 90, 95};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cout << grades[i] << ” “;
}
This loop prints each value in the grades array.
5. Array Size and Limitations
Arrays have fixed sizes, meaning they can only hold a set number of items. If an array has 5 spots, it will only hold 5 items.
Example:
int ages[3] = {10, 12, 14};
Here, ages has only 3 spots, so we cannot add more values.
Conclusion
So, guys, it’s time to wrap up. In this article, we’ve covered Types of Arrays in C++ in detail. I personally recommend practicing with these arrays in simple coding exercises to solidify your understanding.
Don’t hesitate to create your own examples and experiment with different types of arrays. Start coding today and see how arrays can make your programs easier to manage!
FAQs
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions related to the C++ array types:
It might seem easier to use individual variables, but arrays let you manage multiple values together. Imagine trying to track the ages of ten students with ten separate variables—that would be messy! Arrays make it simple to store and access related data as a single unit.
If you access an index that doesn’t exist, like trying to get the fifth element of a four-element array, you can cause an error in your program. This error happens because you’re trying to look in a place where there is no value stored. Always check the size of your array before accessing its elements to avoid this issue.
No, in C++, once you define the size of an array, it cannot change. This can be confusing if you need to store more values later. If you think you might need a different size, consider using a dynamic array or a different data structure like a vector.
Choosing the right type of array can be confusing. If you need to store a list of values, use a one-dimensional array. If you want to organize data in a table format, then a two-dimensional array is a better choice.
Arrays and lists are not the same in C++. Arrays have a fixed size and can only hold values of one type, while lists can grow and hold multiple data types. This difference can make choosing between them confusing, but understanding your data needs can help.
No, C++ arrays cannot hold different data types in one array. This can be confusing if you come from a language that allows mixed types. If you need to store different types, you can use structures or classes instead.
If you forget the index number or make a mistake, it can lead to accessing the wrong element or an error. This mistake can be frustrating when debugging your code. Always double-check your index numbers to ensure you’re accessing the correct elements in your array.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks





